.svg) National Institute of General Medical Sciences |
 |
 |
National Biomedical Resource for |
| ACERT's Service and Collaborative Projects | ||||||
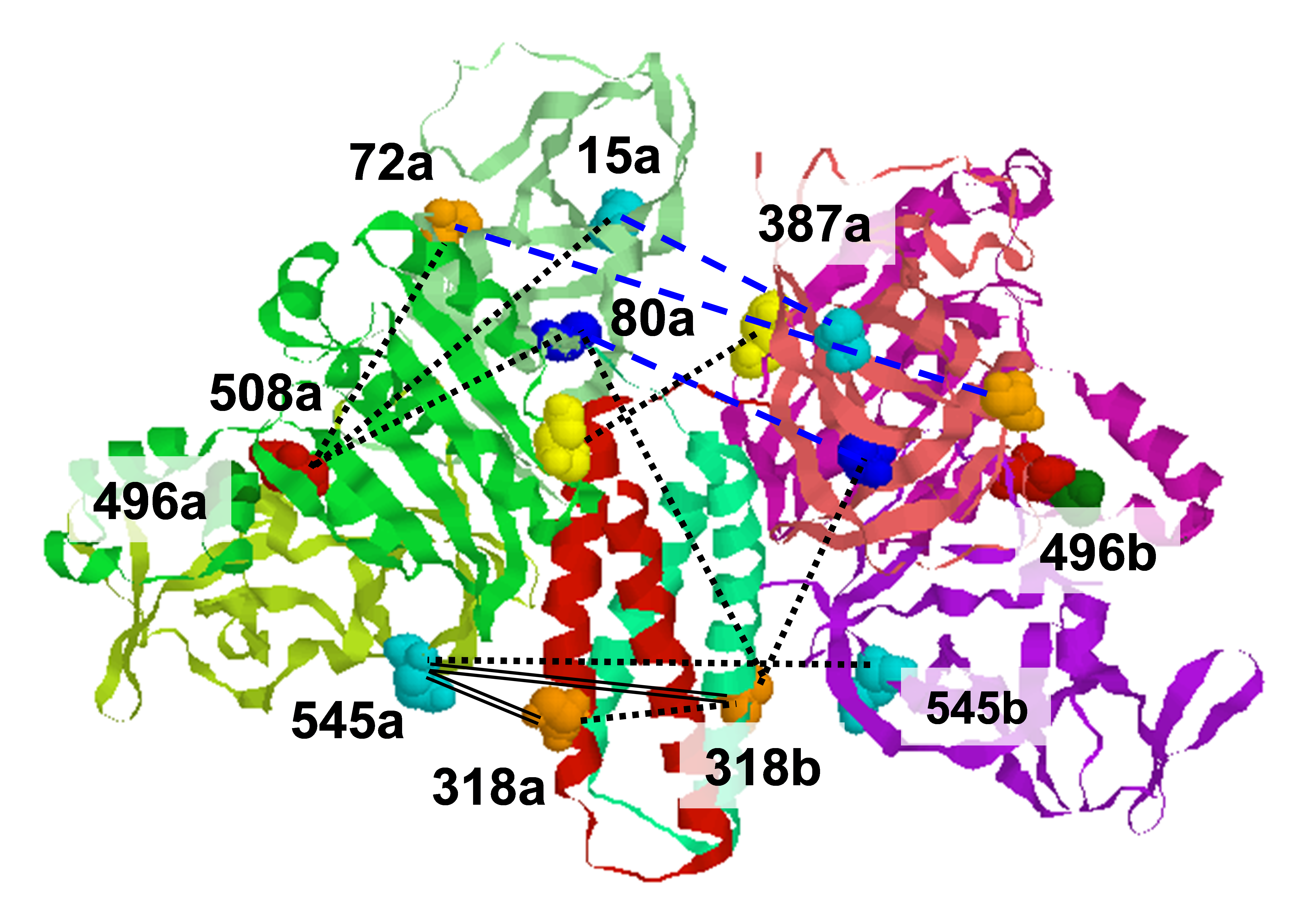
Pulsed dipolar electron spin resonance spectroscopy (PDS) is a powerful tool for measuring distances in solution-state macromolecules. Paramagnetic metal ions, such as Cu2+, are used as spin probes because they can report on metalloprotein features and can be spectroscopically distinguished from traditional nitroxide (NO)-based labels. We demonstrated site-specific incorporation of Cu2+ into non-metalloproteins through the use of a genetically encodable non-natural amino acid, 3-pyrazolyltyrosine (PyTyr). We first incorporated PyTyr in cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) to measure Cu2+-to-NO distances and examined the effects of solvent conditions on Cu2+ binding and protein aggregation. We then applied the method to characterize the complex formed by the histidine kinase CheA and its target response regulator CheY. The X-ray structure of CheY-PyTyr confirms Cu labeling at PyTyr but also reveals a secondary Cu site. Cu2+-to-NO and Cu2+-to-Cu2+ PDS measurements of CheY-PyTyr with nitroxide-labeled CheA provided new insights into the conformational landscape of the phosphotransfer complex and they have implications for kinase regulation. Funding: R01GM066775, R01GM079679, R35GM122535 (BRC); P41GM103521 (JHF); T32GM008267 (GEM); NE-CAT Advanced Photon Source P30GM124165 and S10RR029205. Publication: J. Phys. Chem. B 122, 9443-9451 (2018); PMCID: PMC6215709. |
||||||
|
||||||
| Gregory E. Merz, Peter P. Borbat, Alise R. Muok, Madhur Srivastava, David N. Bunck, Jack H. Freed, and Brian R. Crane (Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY) | ||||||
|
|
About ACERT Contact Us |
Research |
Outreach |
ACERT is supported by grant 1R24GM146107 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), part of the National Institutes of Health. |
|||||
| ||||||||