.svg) National Institute of General Medical Sciences |
 |
 |
National Biomedical Resource for |
| ACERT's Service and Collaborative Projects | |
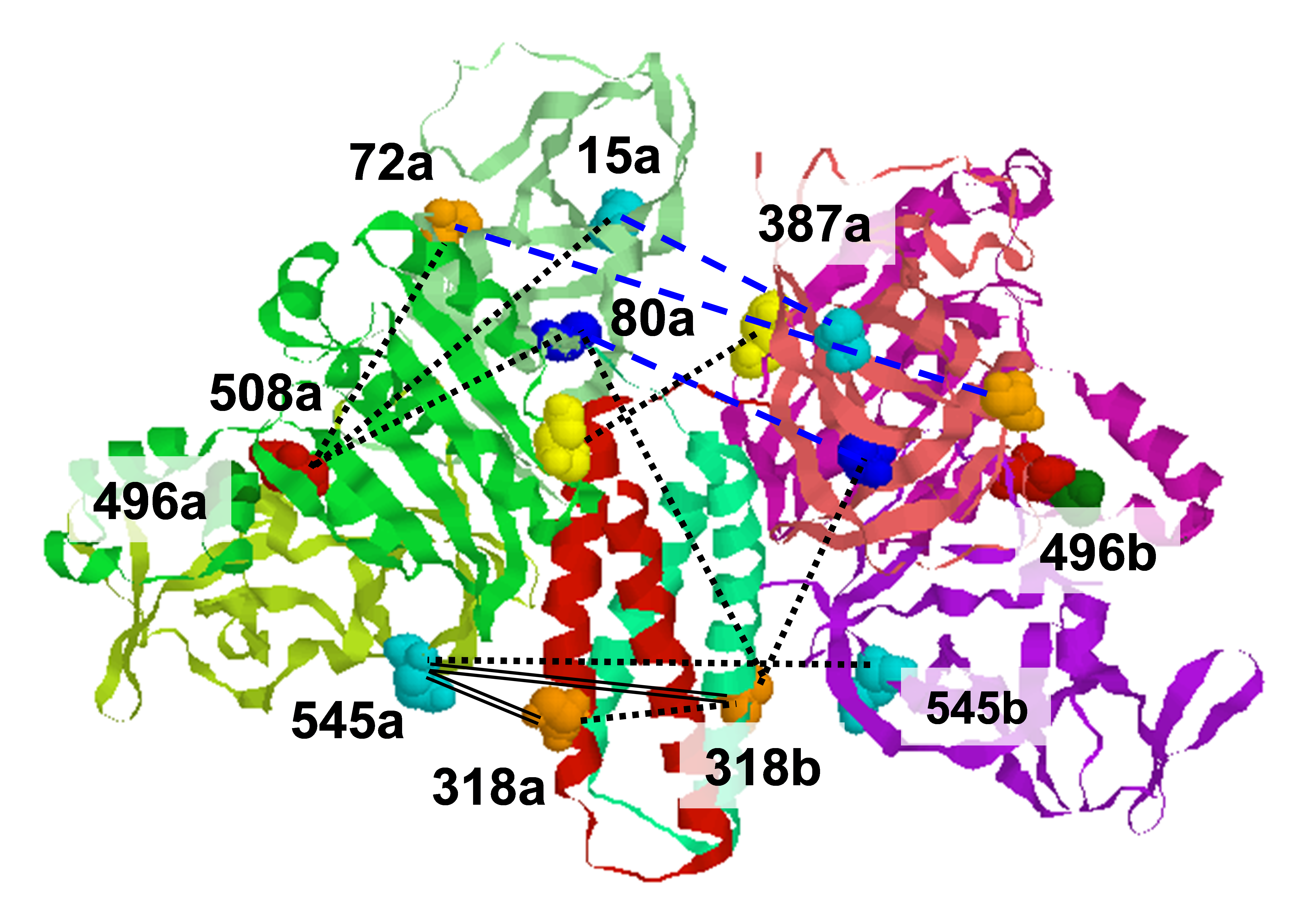
Tau is a microtubule associated protein that is genetically linked to dementia and linked to Alzheimer's disease via its presence in intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangle deposits, where it takes the form of aggregated paired helical and straight filaments. Although the precise mechanisms by which tau contributes to neurodegeneration remain unclear, tau aggregation is commonly considered to be a critical component of tau-mediated pathogenicity. Nevertheless, the context in which tau aggregation begins in vivo is unknown. Tau is enriched in membrane rich neuronal structures such as axons and growth cones, and can interact with membranes both via intermediary proteins and directly via its microtubule-binding domain. Membranes efficiently facilitate tau aggregation in vitro, and may therefore provide a physiologically relevant context for nucleating tau aggregation in vivo. Furthermore, tau-membrane interactions may potentially play a role in tau's poorly understood normal physiological functions. Despite the potential importance of direct tau-membrane interactions for tau pathology and physiology, the structural mechanisms that underlie such interactions remain to be elucidated. We employ electron spin resonance spectroscopy to investigate the secondary and long-range structural properties of the microtubule binding domain (MBD) of three-repeat tau isoforms when bound to lipid vesicles and membrane mimetics. We showed that the membrane interactions of the tau MBD are mediated by short amphipathic helices formed within each of the MBD repeats in the membrane-bound state. We also showed that these individual helical regions behave as independent membrane-binding sites linked by flexible connecting regions (df. Figure). These results represent the first detailed structural view of membrane-bound tau and provide insights into potential mechanisms for membrane-mediated tau aggregation. Furthermore, the results may have implications for the structural basis of tau-microtubule interactions and microtubule-mediated tau aggregation. Relevant Publication: E.R. Georgieva, S. Xiao, P.P. Borbat, J.H. Freed, and D. Eliezer, Biophys. J., 107, 1441-1452 (2014); PMC4167292. |
|
|
|
|
Elka R. Georgieva, Peter P. Borbat, and Jack H. Freed (ACERT) Shifeng Xiao and David Eliezer (Department of Biochemistry and Program in Structural Biology, Weill-Cornell Medical College) |
|
|
|
About ACERT Contact Us |
Research |
Outreach |
ACERT is supported by grant 1R24GM146107 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), part of the National Institutes of Health. |
|||||
| ||||||||